Guide
In the industrial production process, according to different working conditions measurement requirements, it is necessary to design and manufacture temperature instruments of different structural forms. Today, the automation channel will give you a detailed introduction to the structure, selection and precautions of the temperature meter.
Temperature instrument structure
Simple structural forms such as thermocouples consisting only of filaments and insulating tubes, as well as more complex structural forms such as temperature gauges used in open air or in corrosive atmospheres or in explosive environments, require protective tubes and Waterproof junction box or explosion-proof junction box. This article focuses on the basic structure of temperature meters used in open air or in corrosive atmospheres or in explosive environments. The basic structure of the temperature meter mainly includes: junction box, connecting tube, process connection, protection tube, temperature measuring core assembly and electrical interface. As shown in Figure 1. Their related features are detailed below.
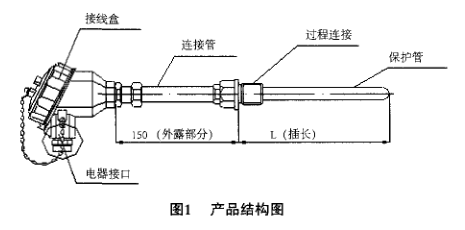
Junction Box
The junction box acts to protect the temperature sensing element from the outside atmosphere and to make the external wires in good contact with the terminal. The housing is waterproof and explosion-proof depending on the environment. For non-explosive hazardous environments, the use of ordinary waterproof housing can meet the requirements of field use; for explosive atmospheres, the instrument must use explosion-proof housing to prevent dangerous situations.
Connecting pipe
The connecting pipe part mainly assembles and connects the casing and the protective pipe part, and is exposed at the installation site, generally providing a length of 150 mm. If the user's on-site space requirements can be lengthened or shortened.
Process connection
Process connection is the key to the on-site installation of the instrument. Generally, threaded and flanged installations are used. The user must specify the installation method and detailed specifications when ordering. For threaded installation, the thread specifications such as M33×2, 1/2NPT, G3/4, R1, etc. must be clearly marked to ensure consistency with the on-site installation thread; for flange installation, the standard category of the flange must be specified (mainly HG, GB, ANSI, SH, etc.), nominal diameter, nominal pressure and sealing surface form, etc., to ensure the consistency of the positive flange of the product configuration and the installation pitch of the field sub-flange.
Protective tube
The protective tube is a key component used by the user and is a device for protecting the sensor temperature sensing element (resistance element or thermocouple element) from mechanical damage and chemical corrosion of the medium. Due to different temperature measurement environment, it is necessary to configure different material protection tubes such as high temperature resistant high temperature alloy protection tube, corrosion resistant PTFE protection tube, and airtight corundum tube; etc.; different pressure protection tubes are required due to different pressures. Such as straight protection tube or conical protection tube.

The protection tube has two major categories: metal protection tube and non-metal protection tube.
Metal protection tube
Under normal circumstances, the metal protection tube is usually made of ordinary stainless steel (304, etc.). When the measured ambient temperature is higher than 900 °C, high-temperature stainless steel such as GH30 and 2520 steel must be used. When the measurement environment is corrosive, anti-corrosion metal is used. Such as 316L, GH30, 2520, Hastelloy, titanium alloy or spray a PTFE protective layer on the metal protection tube (maximum use temperature 240 ° C).
Non-metallic protective tube
The non-metal protection tube mainly has silicon carbide and aluminum oxide protection tubes. The silicon carbide protection tube is mostly used in the wear-resistant measurement environment, and the aluminum oxide protection tube (mainly high-aluminum porcelain tube and corundum tube) is mostly used in the high-temperature measurement environment. Corundum protection tube has good air tightness and is stable below 1700 °C, but it is not suitable for use in hydrogen sulfide environment.
It should be noted that non-metallic protective tubes have poor impact resistance, and such protective tubes should be avoided in environments where the impact of the measuring medium is high. In environments where the medium pressure is high, it is best to configure a tapered protective tube to improve the pressure resistance.
Temperature measuring core assembly
The temperature measuring core component is a key component of the product and is protected from wear or corrosion in the housing and the protective tube. There are common assembly type and armor type (the difference between the common assembly type and the armor type product is in the temperature measuring core assembly). Type). In the case of vibration, the ordinary assembly type thermal resistance element is easily broken and the signal is interrupted, so the product should be prevented from being installed in the vibration measurement environment. In addition, the accuracy level of the temperature sensing element in the temperature measuring core component determines the accuracy level of the whole product, and the temperature sensing component is strictly measured before production and assembly.
Electrical interface
The electrical interface is used by the user when connecting (cable) leads (or compensation wires) in the field, mainly through the compression nut. For ordinary products, the compression nuts of explosion-proof products are different. For explosion-proof products, it is necessary to ensure that the compression nut and the sealing plug tightly press the (cable) leads without gaps to prevent the electric spark from leaking.
Temperature meter selection and precautions
Through the introduction of the above knowledge, the function of each structural component of the product is clarified, and the user needs to select a suitable product for temperature measurement according to the requirements of the site conditions during the selection. When selecting the model, grasp the following principles: when the measurement is lower than 550 °C and the precision is high, the thermal resistance sensor is selected, and the temperature above 550 °C is selected as the thermocouple sensor; according to the design and installation method of the on-site temperature instrument, the appropriate process connection mode is selected; The pressure of the warm medium selects the protection tube of different shapes; according to the particularity of the medium, the protection tube of the corresponding performance is selected.
In order to select faster and better, users should also pay attention to the following:
1) Ordinary assembly type thermal resistance is not suitable for use in a vibration-measuring measurement environment because of its poor vibration resistance.
2) Due to the use of armored wire and armored wire, the special structure of the armored product makes the product flexible and has good vibration resistance, which makes up for the shortage of ordinary assembly products.
3) Explosion-proof products must be used in an explosion-proof environment. Explosion-proof products have good explosion-proof performance. When ordering, it is necessary to select different explosion-proof categories according to the operating environment system explosive mixture, see table. At present, the explosion-proof categories used in industrial production mainly include: ExdIIBT1-T6, Exd 1I CT1-T6, and ExiaIICT1-T6.
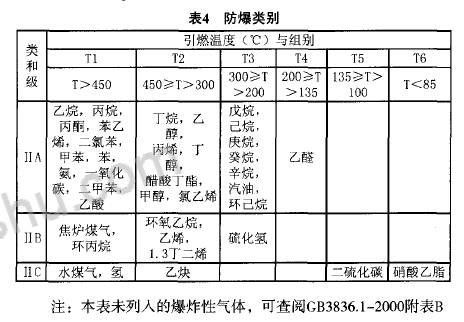
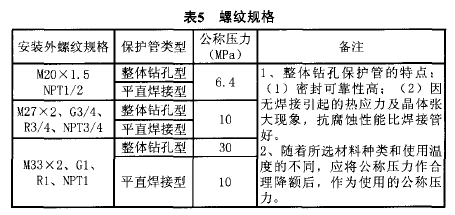
4) Fixed thread protection tube products have different installation thread specifications and different pressures. The detailed data is shown in Table 5.
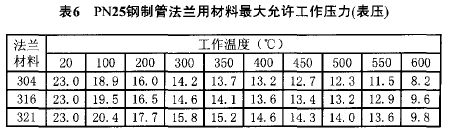
5) For flange-mounted products, when selecting the pressure (PN) grade, it must be considered that the pressure-bearing capacity gradually decreases as the temperature rises. Taking the flange of 304 and PN25 as an example, the bearing pressure is 23.0 MPa at 20%. As the temperature increases, the bearing pressure drops to 8.2 MPa at 600 °C. Part of the material temperature - pressure parameter). In actual selection, the pressure level can be determined by referring to the specific parameters of the pressure-temperature rating in the flange standard to ensure the safety of the overall system design. As shown in Table 6.
Customized Laboratory Testing Instruments
Wuxi Lerin New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.lerin-tech.com