As one of the greatest inventions of human society in the 20th century, computers have gradually entered the post-PC era recently. The arrival of the post-PC era also marked the birth of embedded products, such as mobile phones, PDAs, and CNC machine tools.
China has the world's largest consumer electronics market, and the number of mobile phones, color TVs, VCDs, and household appliances ranks first in the world. With the improvement of the economic level and the change of consumption structure, people have higher and higher requirements for consumer electronic products, such as product flexibility, controllability, durability, high cost performance, etc., which can be embedded in a reasonable and effective manner. System design and optimization to achieve. In addition, modern medical, measurement and control instruments, and electromechanical products have high requirements for system reliability and real-time performance, and require the support of dedicated embedded systems. These requirements have greatly stimulated the development and industry of embedded systems. The process of transformation. The development of embedded systems will further improve the framework of the information industry and become an accelerator for the development of the information industry. As the complexity of embedded systems increases, the coordination of software and hardware is the key to embedded systems.
Definition of embedded system
From the perspective of product application, an embedded system is a device that controls, monitors or assists the operation of equipment and workshops. Many different professionals think and position embedded systems from different perspectives, so there are many definitions of embedded systems.
Embedded systems are based on the current industry and academia’s general views on embedded systems. They are application-centric, computer-based, and software and hardware can be tailored to adapt to the application system’s strict requirements for functionality, reliability, cost, volume, and power Dedicated computer system required.
Embedded hardware system
The hardware platform of most embedded systems. It consists of two parts:
1. A protocol processing module centered on a general-purpose processor for network control protocol processing;
2. A signal processing module centered on a digital signal processor (DSP) for modulation, demodulation and digital/analog signal conversion.
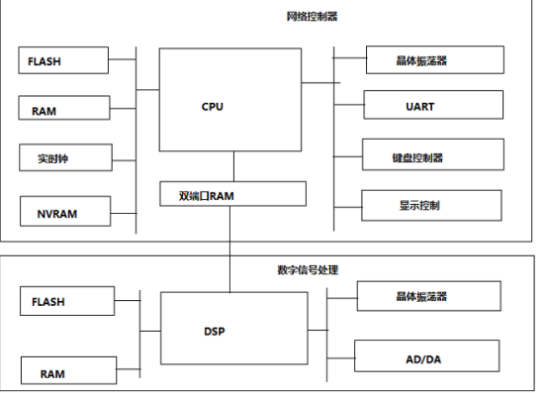
Hardware system structure
The core components of embedded systems are various types of embedded processors. According to incomplete statistics, the total number of types of embedded processors in the world has exceeded 1,000, and there are more than 30 series of popular architectures. Because of the great differences in embedded system design, the choices are diversified.
The power consumption, volume, cost, reliability, speed, processing capacity, electromagnetic compatibility, etc. of embedded processors are all restricted by application requirements. The main factors to consider when choosing a processor are to investigate the CPU suppliers listed on the market, the processing speed of the processor, technical indicators, the low power consumption of the processor, the software support tools of the processor, whether the processor has built-in debugging tools, and the processor. Does the supplier provide evaluation boards, etc.?
Embedded software system
Although embedded systems have extremely broad market demands and development prospects, the development of embedded systems has gone through a tortuous and painful course for many years. With the emergence of microprocessors, low-cost, compact CPU and peripheral connections provide a stable and reliable hardware architecture, so the bottleneck restricting the development of embedded systems is prominent in the software.
From the operating platform, embedded software can be divided into:
1. Software running on the development platform: design, development, testing tools, etc.
2. Software running on embedded systems: embedded operating systems, applications, drivers and some development tools
There are many operating systems that can be used for embedded system software development, but the key to choosing a suitable operating system is to provide those development tools from the operating system, the difficulty of porting the operating system to the hardware interface, the memory requirements of the operating system, and whether the developer is familiar with this The operating system and the API it provides, whether the operating system provides hardware drivers, whether the operating system is tailorable, and the real-time nature of the operating system are considered.
Embedded application software is the key to realize embedded system functions. In order to improve execution speed and system reliability, embedded software is generally solidified in the memory chip or the single-chip microcomputer itself, rather than stored in a carrier such as a disk. The software code requires high quality , High reliability and high real-time.
Features and applications of embedded systems
The hardware and software of the embedded system must be tailored. Compared with the general-purpose processor, the biggest difference of the embedded processor is that most of the work is used in the system designed for a specific user group. It usually has low power consumption and low power consumption. The characteristics of small size and high integration can integrate many tasks inside the chip, which is conducive to the trend of miniaturization of embedded system design and greatly enhances the mobility.
The power consumption, volume, cost, reliability, speed, processing capacity, electromagnetic compatibility, etc. of embedded processors are all restricted by application requirements.
Embedded microprocessor has 4 characteristics:
1. Strong support for real-time multitasking
The embedded system can complete multiple tasks and has a short interrupt response time, thereby reducing the execution time of the internal code and real-time kernel to a minimum.
2. It has a powerful storage area protection function
Because the software structure of the embedded system has been modularized, in order to avoid false cross-effects between software modules, it is necessary to design a powerful storage area protection function, which is also conducive to software diagnosis.
3. Scalable processor structure
The extensible processor structure can quickly develop an embedded microprocessor with the highest performance to meet the application.
4. Very low power consumption
Used in portable wireless and mobile computing and communication devices, the power consumption of battery-powered embedded systems is mW or even μW.
Busbar Built In Current Transformer
Busbar Built In Current Transformer,Mini Busbar Built Current Transformer,Electric Meter Mini Current Transformer,Current Transformer With Busbar Inside
Zibo Tongyue Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.tongyueelectron.com