Complex modern circuits usually contain a large number of components, such as microcontrollers, ICs, DSPs, and FPGAs. Each component has a specific supply voltage requirement. A distributed power system composed of a shared "central" power supply and a large number of local converter modules has become the most energy-efficient solution that can meet this requirement. Until recently, manufacturers have begun to choose discrete devices, especially when they need to be used in large quantities. Due to the steady decline in the price of fully certified modules, these products have now become viable alternatives. At present, this economical module is suitable for almost any application.
It has long been recognized that modular DC/DC converters have higher energy efficiency and reliability, but because of their high cost, manufacturers have not used such converters in their designs, especially when a large number of converters are needed. Although development costs are still increasing, the price of certified modules has dropped significantly compared to previous years. In addition, if you consider other issues such as time to market, modular converters are usually a more cost-effective choice nowadays.
Although most manufacturers have used purchased switch-mode power supplies in their circuits, they generally still hesitate to use third-party DC/DC converters in their designs. There are two main reasons: on the one hand, DC/DC converters work with low DC power, which are relatively simple components; on the other hand, they form part of the printed circuit board, so it is best to use a process and Place other components together.
At first glance, developing a converter seems to be a relatively simple task. But this is an illusion, because devices that usually look simple on the surface are most prone to problems in details. When designing DC/DC converters, some of the characteristics of analog technology usually cause very difficult problems. For example, printed lines will produce capacitance or inductance that does not exist in the circuit diagram, and these capacitances or inductances are usually unpredictable. In addition, the performance of the transformer is not only affected by the ferrite material, but also depends on the hysteresis loop range of the device. This will produce a high level of interference, and it may be necessary to repeat the secondary design. Eventually the product launch was delayed, sometimes for several months. The manufacturer chooses off-the-shelf modules, which not only shortens development time, but also minimizes commercial risks.
The converter module is efficient and practical
Another huge advantage that professional suppliers bring to converter modules is their high efficiency and outstanding reliability. These modules have been verified by thousands of applications. Modern designs usually require a large number of converters, so it is recommended that developers pay close attention to the energy efficiency of each such component. Large converters usually operate at an energy efficiency rating of more than 90%, while small DC/DC converters in the 1 W to 2 W range are difficult to achieve this rated energy efficiency because each converter has a fixed static power consumption, while small converters This type of power consumption ratio of the converter is relatively higher than that of the large converter. Therefore, according to the actual power and topology, the energy efficiency of the optimized DC/DC converter is about 85% to 92%.
But in this case, only paying attention to the absolute rated energy efficiency at full load and not considering the energy efficiency in the lower load range will be dangerous. Generally speaking, all converters can achieve the highest energy efficiency when operating at close to the rated load. The lower the load, the lower the energy efficiency. But well-designed converters have stable and high energy efficiency, especially in the important medium to low load range.
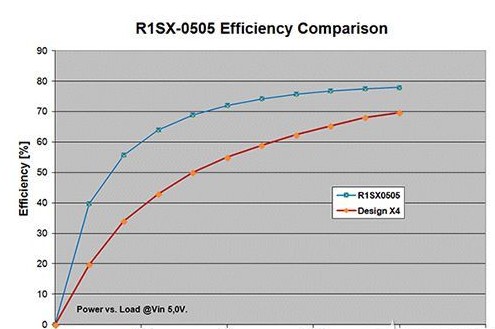
The new R1SX-0505 1 W converter of the size of a nail was tested and compared with a custom converter of the same rated power. There is a huge difference in energy efficiency between the two. At full load, the custom-designed model has reached an acceptable energy efficiency level of approximately 70%. But at half load, the energy efficiency drops to slightly higher than 55%, while the RECOM module can reach 72% energy efficiency even at half load, which is 17% higher (Figure 1). The power loss of the custom-designed device is 409 mW, which is more than double that of the R1SX with a loss of 195 mW. In this case, choosing "off-the-shelf" modules can not only reduce energy consumption, but also reduce the thermal load on the PCB.
Other advantages of modular converters
In addition, modular converters are absolutely leading in terms of size and power density. As the circuit becomes more and more complex, the small footprint on the PCB presents a huge advantage. Usually, the discrete converter in the RECOM module only takes up half of the space. This is a huge advantage because the space on the PCB is getting scarce.
Modular converters also have important advantages in material management. The parts such as toroidal transformers, ferrite cores, chokes and transistors required to produce custom converters are all highly specialized components and are usually not included in the internal parts list. Purchasing "off the shelf" modules can simplify the parts list and make it easier to manage.
Finally, the use of certified components can also greatly accelerate the certification of the final product. To avoid trouble, the final obstacle should be considered as early as possible in the design process. As a leading manufacturer in this field, RECOM has taken another step forward, providing customers with the option of testing products in an internal EMC laboratory before submitting for certification.
in conclusion
If you only compare the cost of components, the price of a discrete converter is generally lower than the price of the purchased module. But when you consider the cost of development, testing, and certification, a different situation will arise. In fact, the price of modular converters has dropped significantly compared to previous years.
These modules use a fully automated production process, with extremely high compactness and reliability. For example, it can work at a temperature of -40°C to +100°C and at full load, and its isolation capacitance is about 40 times higher than competing products. These converters can be used for input/output voltages of 3.3 V or 5 V, with 1 kVDC or 3 kVDC isolation. This series is fully certified by IEC/UL/EN 62368-1 and UL 60950-1, and comes with a three-year warranty.
RAM/RFM electric heating capacitors
RAM/RFM Electric Heating Capacitors
Electric Heating Capacitor,Film Heating Capacitor,Electric Capacitor Bank,Induction Heating Capacitors
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.cndingweitech.com