Fault phenomenon
Possible Causes
Treatment
Immobile or unreliable
1. The power supply voltage is too low or the fluctuation is too large
2. Insufficient operating circuit power supply capacity or disconnection, wiring error and poor contact of control contacts
3. Control power supply voltage does not match coil voltage
4. The product itself is damaged (such as a broken or burnt coil, a mechanically movable part is stuck, the shaft is rusted or skewed, etc.)
5. Contact spring pressure and overtravel are too large
6. The power supply is too far from the contactor and the connecting wires are too thin.
1. Increase the power supply voltage
2. Increase power supply capacity, correct wiring, repair control contacts
3. Replace the coil
4. Replace the coil to eliminate the stuck fault and repair the damaged part
5. Adjust contact parameters as required
6. Replace the thicker connecting wire
Not released or released slowly
1. Contact spring pressure is too small
2. Contact welding
3. The mechanical movable part is stuck, the shaft is rusted or skewed
4. Reaction spring damage
5. There is oil or dust on the pole surface of the iron core
6. E-shaped core, when the end of life, because of the demagnetization
Disappear, the remanence increases, so that the core does not release
1. Adjust contact parameters
2. Eliminate welding faults, repair or replace contacts
3. Eliminate jams and repair damaged parts
4. Replace the reaction force spring
5. Clean the iron core
6. Replace the core
Coil overheated or burnt
1. Power supply voltage is too high or too low
2. Coil technical parameters (such as rated voltage, frequency, load factor and applicable working system, etc.) do not match the actual conditions of use.
3. Operating frequency is too high
4. Poor coil manufacturing or mechanical damage, insulation damage, etc.
5. Special environmental conditions: if the air is humid, contains corrosive gases or the ambient temperature is too high
6. The moving part is stuck
7. The AC core is extremely uneven or the magnetic air gap is too large
8. The AC contactor derives a DC-operated double coil, which causes the coil to overheat because the normally closed interlocking contact is not welded.
1. Adjust the power supply voltage
2. Exchange coil or contactor
3. Choose other suitable contactors
4. Replace the coil to eliminate the fault that caused the mechanical damage of the coil
5. Specially designed coil
6. Eliminate jamming
7. Clear the pole or replace the core
8. Adjust the interlocking contact parameters and replace the burnt coil
Electromagnet (AC) noise
1. Power supply voltage is too low
2. Contact spring pressure is too large
3. The magnetic system is skewed or mechanically stuck so that the core cannot be absorbed
4. The surface of the pole is rusted or adhered to the core by foreign matter (such as grease and dust)
5. Short circuit ring break
6. Iron core pole wear is excessive and uneven
1. Increase operating loop voltage
2. Adjust the contact spring pressure
3. Troubleshoot mechanical jam
4. Clean the iron core
5. Change the core or short circuit
6. Replace the core
Contact welding
1. Operating frequency is too high or product is overloaded
2. Load side short circuit
3. Contact spring pressure is too small
4. Metal particles protruding or foreign matter on the contact surface
5. The operating circuit voltage is too low or mechanically stuck, causing stagnation during the suction process, and the contact is stopped at the position just in contact
1. Exchange the appropriate contactor
2. Eliminate short circuit faults and replace contacts
3. Adjust the contact spring pressure
4. Cleaning the contact surface
5. Improve operating power supply voltage, eliminate mechanical jamming, and make contactor reliable
Eight-hour working contact overheating or burn
1. Contact spring pressure is too small
2. There is oil on the contacts, or the surface is uneven.
Metal particles protruding
3. Ambient temperature is too high or used in a closed control box
4. Copper contacts for long-term work
5. The overtravel of the contact is too small
1. Increase the contact spring pressure
2. Cleaning the contact surface
3. Contactor derating
4. Contactor derating
5. Adjust contact overtravel or replace contact
Short-term internal contact wear
1. The contactor is not properly selected, and the capacity is insufficient in the following cases:
(1) reverse brake
(2) There are more close operations
(3) Operating frequency is too high
2. Three-phase contacts are not in contact at the same time
3. Load side short circuit
4. The contactor cannot be reliably sucked in
1. Contactor derating or use for heavy weight
Task contactor
2. Adjust to contact at the same time
3. Eliminate short circuit faults and replace contacts
4. See the action unreliable treatment
Interphase short circuit
1. The reversible conversion of the contactor interlock is unreliable. Due to the malfunction, the two contactors are put into operation at the same time, causing phase-to-phase short circuit, or the contactor is too fast, the conversion time is short, and an arc short circuit occurs during the conversion process.
2. Dust accumulates or sticks to moisture, grease, and deteriorates insulation.
3. Product parts are damaged (such as arc chute breaking)
1. Check electrical interlocks and mechanical interlocks;
The extension of the intermediate link on the line can be reversed
Change time
2. Clean up often and keep it clean
3. Replace damaged parts
The sensor includes linear encoder and rotary encoder, which is used for the position measurement of speed, displacement and angle. Yuheng optics can provide rotary encoders based on optical, magnetic and gear principles, linear encoders based on optical principles and supporting products.
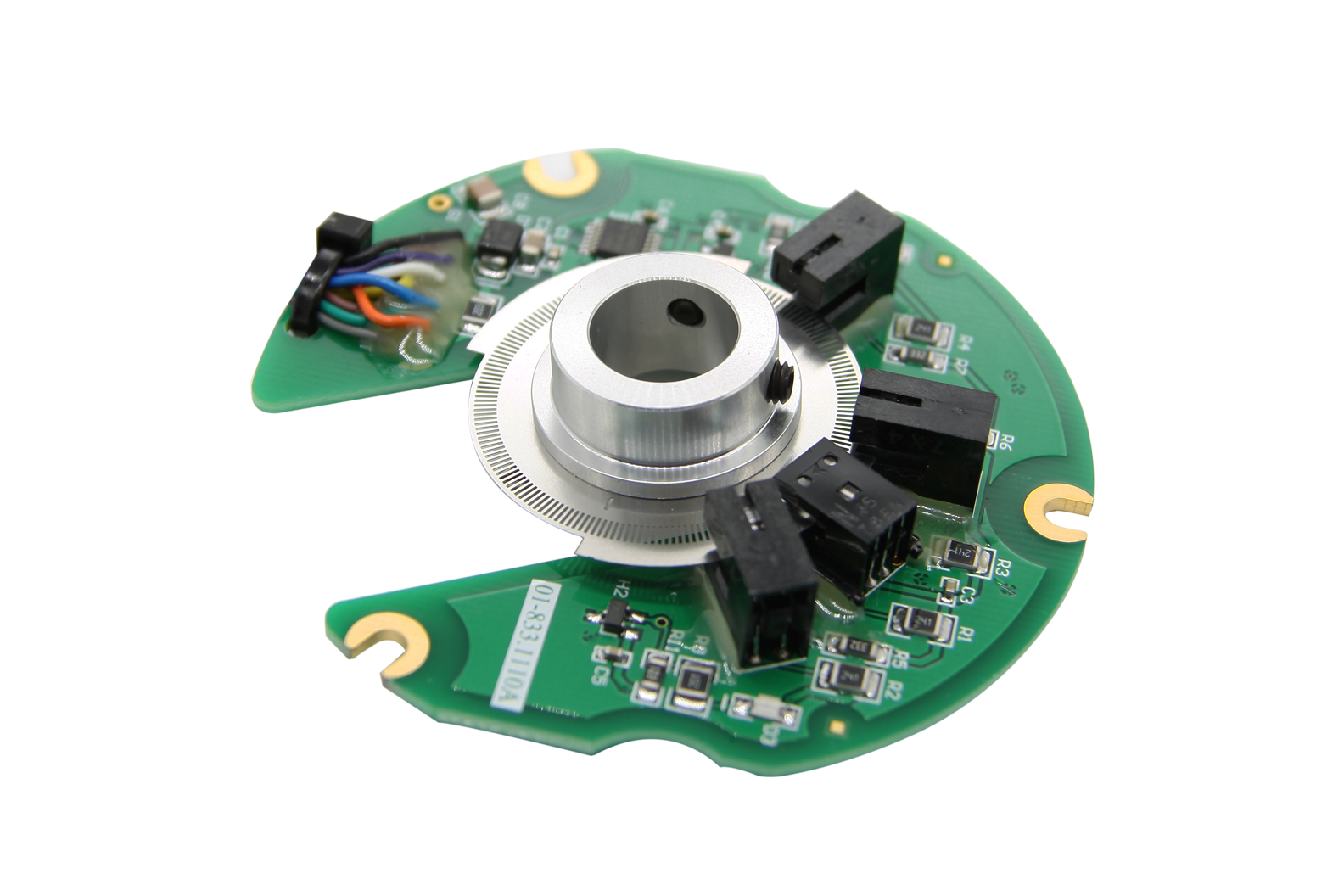
Custom Sensor,Clintegrity Encoder,Absolute Angle Encoder,Small Rotary Encoders
Yuheng Optics Co., Ltd.(Changchun) , https://www.yhenoptics.com