[Source: "High-tech LED-technology and application" February issue Lan Wei]
I. Introduction
At the end of the LED indoor lighting competition, the focus is high index, high light efficiency, that is, double high LED. LED indoor lighting does not have any high-altitude refers to any lighting art, and even LED lights can not compete with ordinary lighting. High-intensity refers to the preparation of a variety of phosphors, and many phosphors have multiple absorption and excitation problems, resulting in low light efficiency. In fact, the dual 80 LED (80, 80) makes many experienced engineers unable to find the North (of course, the contrast color R1 to R15 with powder).
Second, the mathematical model of single powder with powder in the case of imitation lumen products
For the imitation lumen series, the color temperature will be significantly changed after the sealant is injected. The following is added: the final product is the relative starting point. It is assumed that the interface reflection amount of the sealant and the fluorescent glue is 0 after the injection, and the semi-finished fluorescent glue is on the air. Interfacial reflection loss is K%
1. Single powder powder mathematical model 1QCH=-LnZ0 Q is the color shift factor, C is the concentration, H is the thickness of the fluorescent glue, and Z is the hundred parts of the blue light.
2. The color shift factor can be corrected in the experiment by the following method: before the sealant is injected, the final blue light is Z0 (1-K%). Among them, K is the interface loss of the finished fluorescent glue.
If the blue ink is Z0, then Z0(1-K%)=Z (where Z is the amount of blue light without the sealant). Since the color temperature of the semi-finished and finished products is measurable, it can be solved. The interface consumes the K value.
Third, the two kinds of phosphor mixed powder with our most common solution method:
"Decompose unfamiliar problems into resolved problems." First, in order to simplify the mathematical model, the mutual excitation and absorption between the phosphors is neglected, so that the excitation of each phosphor can directly apply the mathematical model of the single powder.
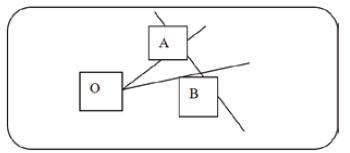
For the same phosphor thin layer, the A phosphor and the B phosphor are excited by the same proportion of blue light. The same blue light ratio is a straight line with a 135 degree angle in CIE1931 chromaticity coordinates, and there is an intersection with the phosphor powder concentration trend line, as shown in the following figure:
OA is the trend line of A phosphor powder concentration, OB is the trend line of B powder single powder concentration, OC is the mixed powder trend line, AB means that the two phosphors are excited by the same proportion of blue light.
The coordinates of the three points A, B, and C are (XA, XB), (XB, YB), (XC, YC), and have the following relationship: QACAH=QBCBH=QCCCH=-LnZ
You can imagine a situation where the concentration of CC phosphor is a mixture of K-concentration of CA and a concentration of (1-K) CB. Then there are:
CC=CAK+CB(1-K)
Then there are:
QC=QACA/[(CA-CB)K+CB];
Since the light at point C is synthesized by the light of point A of K and the light of point B of (1-K), the complementary color theorem is obtained:
K / ( 1 - K ) = ( XC - XA ) / ( XB -XC); where X is the color coordinate: K = (XC - XA) / (XB - XA); XC, XB, XC is the coordinate point The X-axis value; obviously, if we know the coordinates of the first C point, it is easy to calculate the ratio of A powder and B powder. It is also easy to calculate its color shift factor.
For more information, please refer to the February issue of "High-tech LED-Technology and Applications" magazine.
I. Introduction
At the end of the LED indoor lighting competition, the focus is high index, high light efficiency, that is, double high LED. LED indoor lighting does not have any high-altitude refers to any lighting art, and even LED lights can not compete with ordinary lighting. High-intensity refers to the preparation of a variety of phosphors, and many phosphors have multiple absorption and excitation problems, resulting in low light efficiency. In fact, the dual 80 LED (80, 80) makes many experienced engineers unable to find the North (of course, the contrast color R1 to R15 with powder).
Second, the mathematical model of single powder with powder in the case of imitation lumen products
For the imitation lumen series, the color temperature will be significantly changed after the sealant is injected. The following is added: the final product is the relative starting point. It is assumed that the interface reflection amount of the sealant and the fluorescent glue is 0 after the injection, and the semi-finished fluorescent glue is on the air. Interfacial reflection loss is K%
1. Single powder powder mathematical model 1QCH=-LnZ0 Q is the color shift factor, C is the concentration, H is the thickness of the fluorescent glue, and Z is the hundred parts of the blue light.
2. The color shift factor can be corrected in the experiment by the following method: before the sealant is injected, the final blue light is Z0 (1-K%). Among them, K is the interface loss of the finished fluorescent glue.
If the blue ink is Z0, then Z0(1-K%)=Z (where Z is the amount of blue light without the sealant). Since the color temperature of the semi-finished and finished products is measurable, it can be solved. The interface consumes the K value.
Third, the two kinds of phosphor mixed powder with our most common solution method:
"Decompose unfamiliar problems into resolved problems." First, in order to simplify the mathematical model, the mutual excitation and absorption between the phosphors is neglected, so that the excitation of each phosphor can directly apply the mathematical model of the single powder.
For the same phosphor thin layer, the A phosphor and the B phosphor are excited by the same proportion of blue light. The same blue light ratio is a straight line with a 135 degree angle in CIE1931 chromaticity coordinates, and there is an intersection with the phosphor powder concentration trend line, as shown in the following figure:
OA is the trend line of A phosphor powder concentration, OB is the trend line of B powder single powder concentration, OC is the mixed powder trend line, AB means that the two phosphors are excited by the same proportion of blue light.
The coordinates of the three points A, B, and C are (XA, XB), (XB, YB), (XC, YC), and have the following relationship: QACAH=QBCBH=QCCCH=-LnZ
You can imagine a situation where the concentration of CC phosphor is a mixture of K-concentration of CA and a concentration of (1-K) CB. Then there are:
CC=CAK+CB(1-K)
Then there are:
QC=QACA/[(CA-CB)K+CB];
Since the light at point C is synthesized by the light of point A of K and the light of point B of (1-K), the complementary color theorem is obtained:
K / ( 1 - K ) = ( XC - XA ) / ( XB -XC); where X is the color coordinate: K = (XC - XA) / (XB - XA); XC, XB, XC is the coordinate point The X-axis value; obviously, if we know the coordinates of the first C point, it is easy to calculate the ratio of A powder and B powder. It is also easy to calculate its color shift factor.
For more information, please refer to the February issue of "High-tech LED-Technology and Applications" magazine.

Application: Automobile Wire Harness
Place of Origin:Dongguan, China (Mainland)
Gauge: AWG 28 to AWG 16
Length: Customized
A perfect replacement of the broken or old windshield washer nozzle
Connector: Molex, JST, TYCO, AMP, JAM, KET,Amphenol, Wago,Weidmuller, Phoenix,
Wires & Cables: UL, VDE standards
Inspection: 100% inspection before delivery
Certification UL, IATF16949, CE,
Features:
Superior plastic material. High quality and new brand
Working well with the washer wiper
Easy to install. Reliable craft
Durable. Not easy to be blocked by water
Car Wiper Blades,Obd Jumper Harness,Electrical Cable Gland,Auto Wiper Blade
Dongguan YAC Electric Co,. LTD. , https://www.yacentercns.com